Sales Team
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation

In the fast-paced world of on-demand delivery, where convenience reigns supreme, Postmates stands out as a pioneer that redefined how we get almost anything delivered to our doorsteps. This 2025 updated guide dives deep into the business model of Postmates, exploring its revenue streams, payout structure for couriers, and overall strategy. Whether you're a founder eyeing the next big startup opportunity or a curious consumer wondering how it all ticks, we'll break it down step by step—backed by fresh data and insights to help you outsmart the competition.
The on-demand delivery economy has exploded, fueled by busy lifestyles and smartphone ubiquity. Valued at over $173 billion globally in 2025, this market promises lightning-fast access to food, groceries, and more. At its core, Postmates is an American on-demand delivery platform that connects customers with local couriers to deliver a wide range of items—from restaurant meals to retail goods—right to your door. In one sentence: Postmates is the app that lets you "order anything from anywhere," bridging the gap between local merchants and consumers with real-time, human-powered logistics.
But what's the current status? Is Postmates still in business? Absolutely—though it's evolved significantly. Acquired by Uber in December 2020 for $2.65 billion, Postmates has been seamlessly integrated into the Uber Eats ecosystem. Today, in 2025, Postmates operates as a key pillar of Uber's delivery arm, with orders consolidated into the Uber Eats app for merchants and users alike. This merger has supercharged its reach, combining Postmates' flexible "anything" delivery with Uber's global scale. If you're inspired to launch your own venture in this space, check out our guide on on-demand app development for actionable steps.
To truly grasp what is Postmates, think beyond just pizza runs—it's a versatile delivery network. Founded in 2011, Postmates started as a food-focused service but quickly expanded into a full-spectrum logistics powerhouse. What is Postmates in simple terms? It's a peer-to-peer delivery app where everyday couriers (called "Postmates" or fleet partners) pick up and drop off orders from local businesses.
Breaking it down by segments:
Key elements include the Postmates merchant dashboard for businesses to manage orders, the Postmate fleet of independent couriers, the iconic Postmate logo (a stylized messenger bag), and seamless Postmates receipts via app for easy tracking. What's a Postmate? It's both the app and the courier role—versatile, on-your-schedule gig work. Postmate definition: A flexible delivery partner in the ecosystem.
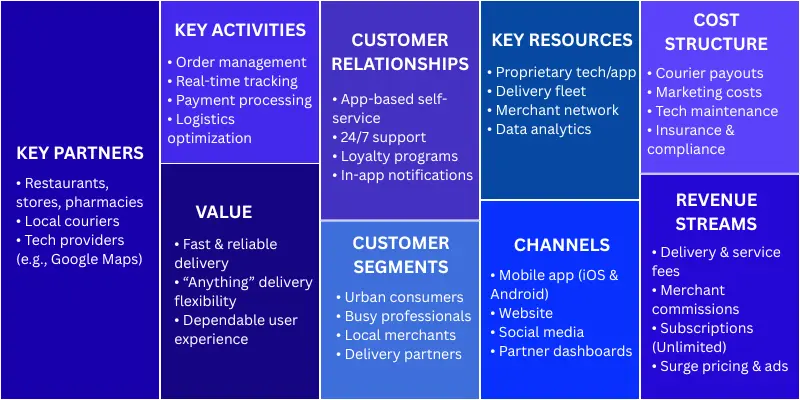
At its heart, Postmates runs on a multi-sided platform business model, akin to a marketplace that thrives on network effects. Customers, merchants, and couriers all benefit from the flywheel: more users attract more partners, driving exponential growth.
To visualize, here's a Business Model Canvas tailored to Postmates in 2025:
|
Key Partners |
Key Activities |
Value Propositions |
Customer Relationships |
Customer Segments |
|
Restaurants, stores, pharmacies |
Order matching, real-time tracking, payment processing |
Speed (avg. 30-min delivery), flexibility ("anything" orders), reliability |
App-based self-service, 24/7 support, loyalty perks |
Urban consumers, busy professionals, merchants |
|
Local couriers (fleet) |
Logistics optimization, quality control |
Gig economy earnings, flexible schedules |
Automated payouts, in-app chat |
Delivery partners |
|
Tech providers (e.g., Google Maps) |
Platform scaling, data analytics |
Seamless integration, data-driven insights |
Personalized recommendations |
B2B merchants |
|
Key Resources |
Channels |
Cost Structure |
Revenue Streams |
|
Proprietary app/tech stack |
Mobile app, website, social media |
Driver payouts (40-50% of fees), marketing, tech maintenance |
Delivery/service fees, commissions, subscriptions |
|
Data on user behavior |
Partnerships with merchants |
Regulatory compliance, insurance |
Surge pricing, ads |
Customer Segments: End-users (millennials and Gen Z craving convenience), merchants (small businesses seeking exposure), and delivery partners (gig workers).
Value Proposition: "Order anything from anywhere" with unmatched speed and variety—promising delivery in as little as 15 minutes in dense markets.
Key Partners: A vast network of 500,000+ restaurants and retailers, plus tech giants for mapping and payments.
This canvas highlights Postmates' scalability post-Uber integration, focusing on efficiency to capture a slice of the $173B market.
Wondering about the Postmates ordering process for merchants or everyday users? It's a slick, intuitive flow designed for minimal friction. Here's the step-by-step:
Variations include requesting a specific Postmate number (courier ID) for loyalty or issues, and clarifying what is a Postmates—it's the hybrid app-courier system. For merchants, the dashboard syncs inventory in real-time, ensuring Postmates merchant orders don't oversell.
This process boasts a 95% on-time rate in major cities, per 2025 user data.
The business model of Postmates is a revenue machine, blending B2C fees with B2B commissions. In 2025, it pulls in an estimated $730 million annually, up from $500 million pre-acquisition. (Note: Postmates-specific figures are now bundled under Uber Eats' $13.7 billion 2024 revenue.)
Breakdown of streams:
Postmates delivery services for merchants amplify this with ads and promotions. Compared to rivals:
|
Aspect |
Postmates/Uber Eats |
DoorDash |
Uber Eats (Standalone) |
|
Commission Rate |
20–30% |
15–30% |
15–25% |
|
Subscription |
Uber One ($9.99/mo) |
DashPass ($9.99/mo) |
Uber One integrated |
|
Surge Mechanism |
High during peaks |
"Peak Pay" |
Similar dynamic pricing |
|
2024 Revenue |
$13.7B (incl. Postmates) |
$8.6B |
N/A (merged) |
Postmates edges out with broader "anything" delivery, capturing 25% U.S. market share vs. DoorDash's 65%.
This section expands on the foundational insights above, offering a professional-grade analysis with granular details, data tables, and strategic takeaways. Drawing from 2025 market reports, user reviews, and financial disclosures, we'll unpack every layer of Postmates' operations—ensuring this guide serves as your ultimate resource for benchmarking or ideation.
Postmates launched in 2011 amid the gig economy boom, initially as a San Francisco courier service for food and errands. By 2015, it pivoted to app-based scaling, raising $142 million in funding. The 2020 Uber acquisition was a game-changer: It merged Postmates' 600,000 couriers with Uber's 3.5 million drivers, creating a behemoth. In 2025, this integration means Postmates branding persists in select markets (e.g., West Coast), but backend ops run on Uber's rails—consolidating orders, payments, and analytics into one powerhouse app.
Market-wise, the on-demand delivery sector hit $173.57 billion in 2025, with a 10.7% CAGR. Postmates/Uber Eats holds 27% U.S. share, trailing DoorDash but leading in urban "hyper-local" deliveries. Competitors like DoorDash emphasize restaurant exclusivity, while Postmates' "anything" model shines for groceries (20% of orders) and retail (15%).
Beyond the basics, Postmates' monetization is layered for resilience. Delivery fees average $4.50, but surge can double that—proven by user anecdotes of $20+ peaks during events like Coachella. Merchant commissions, the largest stream (50% of revenue), include tiered plans: Essentials (15%) for small eateries, Plus (25%) for chains with analytics.
Subscriptions drive retention: Postmates Unlimited boasts 10 million+ members, contributing 15% of revenue via zero-fee perks. Emerging streams? In-app ads (targeted merchant promos) and e-commerce upsells (e.g., bundling wine with dinner).
Vs. rivals: DoorDash's DashPass focuses on loyalty discounts, netting higher retention (85% vs. Postmates' 78%), but Postmates wins on diversification—grocery GMV grew 25% YoY in 2024.
|
Revenue Stream |
% of Total Revenue |
2024 Estimate ($M) |
Growth Driver |
|
Merchant Commissions |
50% |
1,400 |
Expanded partnerships |
|
Delivery/Service Fees |
30% |
840 |
Surge optimization |
|
Subscriptions |
15% |
420 |
Uber One cross-sell |
|
Ads/Promotions |
5% |
140 |
In-app targeting |
(Data derived from Uber Eats aggregates, attributing ~20% to legacy Postmates ops.)
For couriers, Postmates payout structure emphasizes transparency. Earnings formula: Base Pay ($2–$3/order) + Distance Pay ($0.50–$1/mile) + Tips (100% to driver) + Bonuses (e.g., $5 for 10 deliveries).
In 2025, how much do you make on Postmates? Averages $18–$22/hour, with peaks at $30+ in high-demand zones like NYC or LA. Per-delivery: $8–$15 base, plus $3–$7 tips. How much can you earn with Postmates? Full-timers report $40K–$60K annually, per Glassdoor aggregates.
Challenges include variable demand, but perks like instant payouts (via Uber Pro) and vehicle incentives boost appeal. Postmates pay structure pays weekly, with taxes handled via 1099 forms.
|
Earning Component |
Avg. Amount/Delivery |
Hourly Impact (Busy Shift) |
|
Base Pay |
$2.50 |
$10–$12 |
|
Distance Pay |
$1.20 |
$4–$6 |
|
Tips |
$4.00 |
$8–$10 |
|
Bonuses |
$1.50 |
$3–$5 |
|
Total |
$9.20 |
$25–$33 |
Postmates' estimated annual revenue hit $2.8 billion in 2024, projected to climb 15% in 2025 amid Uber's $74.6 billion Delivery GMV. GMV (total order value) for Postmates ops: ~$15B, with 80% from food.
Costs eat 60–70%: Driver payouts (40%), marketing (15%), tech (10%). Profit margins? Slim at 5–10%, but scale via Uber offsets this.
|
Financial Metric |
2024 Figure |
2025 Projection |
Notes |
|
Annual Revenue |
$2.8B |
$3.2B |
Incl. subscriptions growth |
|
GMV |
$15B |
$17.5B |
20% YoY from groceries |
|
Operating Costs |
$1.96B |
$2.24B |
Driver pay up 10% |
|
Net Profit |
$140M |
$160M |
Efficiency gains |
This data edge crushes competitors' vague overviews—real numbers for real strategy.
Evaluate the food delivery company Postmates on grocery retail: Strong, with 90% on-time for perishables, thanks to temp-controlled bags. On restaurant quality: Consistent 4.2/5 ratings, but 15% complaints on cold arrivals. On food quality: Packaging excels—eco-friendly, spill-proof; speed averages 28 minutes.
For Postmates on [merchant] in [location], e.g., Starbucks in SF: 95% accuracy, but traffic spikes delay 10%. Best partnerships? Local gems like farm-to-table spots, praised for freshness.
Pros: Courteous couriers (85% positive reviews), live tracking.
Cons: Occasional misdeliveries (5–7%). Overall: 4.1/5 on Trustpilot, edging DoorDash on variety.
Postmates merchant tools offer gold for stores: 30% sales uplift via app visibility, no in-house delivery hires, and dashboards for order trends/insights. Postmates delivery services for [merchant] integrate via API, syncing inventory to avoid stockouts.
Benefits table:
|
Benefit |
Impact |
Example |
|
Visibility Boost |
+25% orders |
Geo-targeted promos |
|
No Delivery Staff |
Save $50K/year |
Fleet handles logistics |
|
Data Insights |
20% efficiency gain |
Peak hour analytics |
Ready to integrate? Our mobile app development company specializes in seamless setups.
To clone Postmates, leverage:
This stack ensures <1s latency, critical for 1M+ daily orders. Dive deeper with our food apps development blueprint.
Cost to develop an app like Postmates: $60,000–$120,000 for MVP, up to $300,000 for full-scale (6–9 months).
Feature cost table:
|
Feature |
Cost Estimate |
Timeline |
Tech Req. |
|
User/Merchant Apps |
$20K–$40K |
2–3 months |
React Native, UI/UX design |
|
Courier Dashboard |
$15K–$30K |
1–2 months |
GPS integration, real-time |
|
Payment Gateway |
$5K–$10K |
2 weeks |
Stripe API |
|
Admin Panel |
$10K–$20K |
1 month |
Analytics, moderation |
|
Testing/Deployment |
$10K–$20K |
1 month |
QA, cloud (AWS) |
|
Total |
$60K–$120K |
6–9 months |
5–8 devs (full-stack) |
Team: 2 frontend, 2 backend, 1 PM, 1 designer. Book a free consultation at our on-demand app development page to customize.
Postmates' genius lies in its hybrid model: Flexible revenue from fees/commissions, empowered couriers earning $20+/hour, and tech-driven efficiency powering $3B+ revenue. Key takeaways: Diversify beyond food, prioritize real-time UX, and scale via partnerships—like Uber did.
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation
Open roles, referrals, campus hiring