Sales Team
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation

For more than a decade, CRM systems have promised efficiency. Yet in reality, most US sales teams still spend hours updating records, logging calls, qualifying leads manually, and building reports that should already exist. The modern sales stack became bigger — but not smarter.
In 2026, that changes.
A new shift is redefining how revenue teams operate: Agentic AI in CRM. Unlike traditional automation that simply follows predefined rules, agentic systems make contextual decisions, initiate actions independently, and continuously optimize outcomes. Instead of reminding a rep to follow up, the system analyzes buyer behavior, drafts a personalized message, schedules the outreach, and adapts the strategy based on engagement signals.
This evolution is giving rise to a new category of AI-powered CRM software — platforms that don’t just store data but act on it. For sales leaders facing rising acquisition costs, longer deal cycles, and higher revenue accountability, traditional CRM automation for sales teams is no longer enough. Efficiency is no longer the goal. Autonomy is.
Across SaaS, fintech, healthcare technology, and enterprise services in the United States, forward-thinking companies are shifting from workflow automation to fully autonomous CRM systems. The focus is no longer on reducing clicks — it’s on delegating decisions.
This article explores how US sales teams are transitioning from manual CRM management to intelligent, self-operating revenue systems — and what it takes to build, adopt, and scale Agentic AI in CRM successfully in 2026.
To understand why this shift matters, we must first define what makes Agentic AI in CRM fundamentally different from traditional automation.
For years, CRM systems relied on rule-based logic:
That’s automation.
But automation follows instructions.
Agentic systems pursue outcomes.
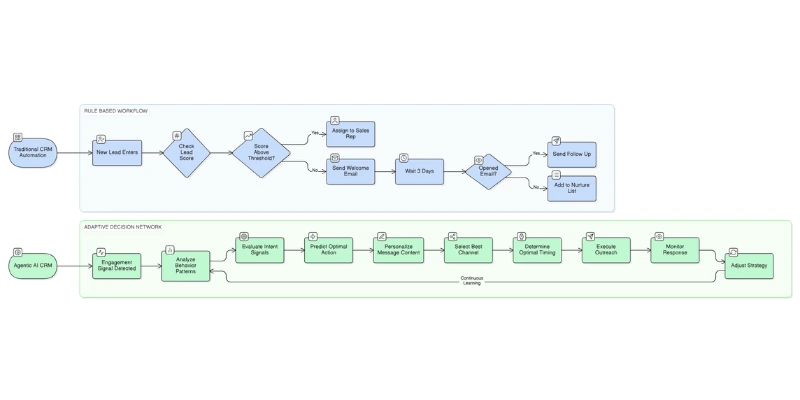
Traditional CRM automation reduces repetitive work. However, it still depends heavily on human input, manual triggers, and predefined workflows. Sales teams remain responsible for interpreting signals, making decisions, and adjusting strategy.
Autonomous CRM systems, on the other hand, operate with goal-driven intelligence. They are built on AI agents capable of:
Instead of waiting for a rule to trigger, an AI agent proactively evaluates pipeline health, detects deal risk, identifies engagement gaps, and initiates corrective action.
This is where AI agents for sales become transformative. They are not scripts. They are adaptive digital teammates.
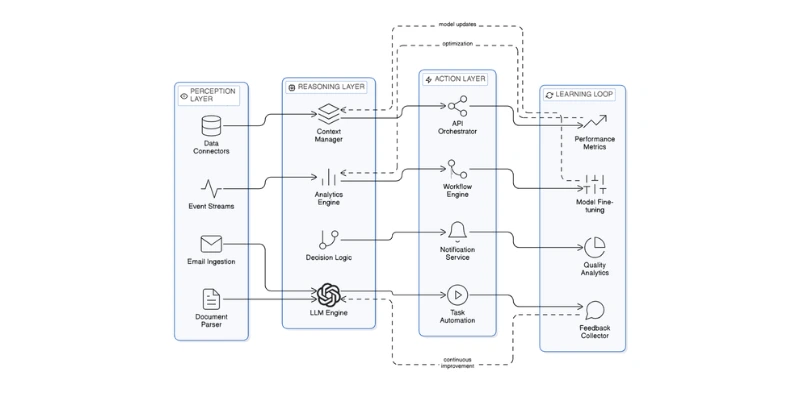
Modern AI-powered CRM software in 2026 typically includes four foundational layers:
Collects and interprets data from emails, calls, CRM entries, calendars, and third-party platforms.
Large Language Models (LLMs) and decision engines analyze context, buyer intent, and probability models.
The system executes tasks — sending emails, adjusting lead scores, scheduling meetings, generating reports, or escalating deals.
Outcomes are fed back into the system to refine decision accuracy and improve future performance.
Together, these layers power what we now call Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 — systems that function less like databases and more like autonomous revenue engines.
|
Capability |
Traditional CRM |
AI-Powered CRM Software |
Agentic AI in CRM |
|
Data Storage |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Rule-Based Automation |
Limited |
Advanced |
Advanced |
|
Predictive Insights |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Autonomous Decision-Making |
No |
Limited |
Yes |
|
Multi-Step Task Execution |
Manual |
Semi-Automated |
Fully Contextual & Adaptive |
|
Continuous Self-Optimization |
No |
Partial |
Built-In |
The key distinction is intent. Traditional platforms store information. AI-enhanced platforms analyze information. But Agentic AI in CRM acts on information with autonomy aligned to revenue goals.
In increasingly competitive US markets, incremental efficiency gains are no longer enough. Sales teams need systems that:
This is not about replacing sales teams. It is about augmenting them with autonomous execution capacity.
In essence, Agentic AI in CRM transforms the CRM from a passive system of record into an active system of execution.
The shift toward Autonomous CRM systems in the United States is not a trend driven by hype. It is a structural response to growing sales complexity, revenue pressure, and operational inefficiency.
In 2026, American sales teams are operating in a fundamentally different environment than they were even three years ago. Buyer journeys are longer, stakeholders are more informed, competition is AI-enhanced, and revenue predictability is under constant scrutiny from boards and investors.
Manual CRM workflows simply cannot keep up.
Modern B2B sales cycles in the US often involve:
Traditional CRM automation for sales teams relies on linear workflows. But real-world buying behavior is nonlinear.
This is where AI-driven sales workflow automation becomes critical. Instead of reacting to isolated triggers, autonomous systems evaluate:
Then they dynamically adjust follow-ups, prioritize outreach, and recommend next steps — often before a human rep recognizes the need.
In industries like SaaS, fintech, cybersecurity, and healthcare technology, this shift is already separating high-growth companies from stagnant ones.
US companies in 2026 operate in an environment of capital efficiency. Growth is still important — but predictable growth is essential.
CROs and RevOps leaders are under pressure to:
Traditional dashboards show data. They do not prevent problems.
AI-powered CRM software equipped with agentic capabilities can:
This is a major reason why Agentic AI in CRM is gaining executive-level attention. It reduces human bias in forecasting and creates a more resilient revenue engine.
Another driving force is economic reality.
In the US:
Sales representatives spend a significant portion of their time on:
These tasks do not directly generate revenue.
By deploying AI agents for sales, companies are shifting routine pipeline management to intelligent systems. The result:
This is not about replacing human sellers — it is about augmenting them with autonomous support that scales without burnout.
Perhaps the most powerful driver is competitive asymmetry.
Organizations that adopt Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 are already seeing:
As AI adoption spreads across US tech companies, late adopters risk structural disadvantage. We are seeing parallels with early cloud adoption in the 2010s — once the shift happens, it becomes irreversible.
Companies exploring broader AI Agent Adoption in tech companies strategies are increasingly integrating CRM autonomy as a foundational layer, not an experimental add-on.
The move toward autonomous CRM systems is not just a technological upgrade. It represents a redefinition of how revenue operations function.
Manual CRM management creates operational friction.
Basic automation creates efficiency.
But Agentic AI in CRM creates leverage.
In 2026, leverage — not labor — is the new competitive advantage in US sales.
Moving toward Agentic AI in CRM is not a switch you flip overnight. For US companies, especially mid-market and enterprise organizations, the transition from manual workflows to Autonomous CRM systems happens in structured phases.
The companies succeeding in 2026 are not replacing their CRM. They are evolving it.
Below is a proven transition framework.
Before implementing AI, organizations must first identify where manual friction exists.
This phase includes:
Typical high-friction areas include:
This diagnostic stage ensures that CRM automation for sales teams aligns with measurable operational pain points rather than vague innovation goals.
US RevOps leaders increasingly treat this phase as a revenue audit rather than a technology upgrade.
The second stage introduces structured automation — but with intelligence layered on top.
This is where AI sales automation tools are integrated into existing systems.
Common implementations include:
At this stage, the CRM remains human-supervised. However, AI-powered CRM software begins influencing decision-making rather than simply logging activity.
This is the bridge between automation and autonomy.
Once assisted intelligence is stable, companies begin deploying AI agents for sales that operate semi-independently.
Examples of task-level AI agents:
Unlike traditional automation triggers, these agents evaluate context continuously.
This marks the beginning of real AI-driven sales workflow automation — where systems initiate action instead of waiting for manual prompts.
At this stage, organizations move beyond isolated AI features and implement coordinated agent networks.
Here’s what changes:
Multiple AI agents collaborate under defined revenue goals.
For example:
A prospect engagement agent detects renewed interest → signals the pipeline prioritization agent → triggers personalized follow-up → alerts the account executive → updates forecasting models.
This is what defines Autonomous CRM systems in 2026.
The CRM evolves from a system of record into a system of execution.
The final stage is not just automation — it is strategic delegation.
Here, Agentic AI in CRM systems:
This level of sophistication often requires deeper architectural planning and alignment with broader AI strategies, including:
Organizations serious about building an agentic AI powered CRM treat it as infrastructure — not a feature layer.
The transition from manual to autonomous does not eliminate human oversight. It shifts the human role from executor to strategist.
Sales reps focus on relationship-building.
Managers focus on coaching.
Executives focus on revenue architecture.
Meanwhile, intelligent systems handle:
This is why Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 are no longer viewed as experimental tools. They are becoming operational foundations.
The companies leading this transformation understand one simple truth:
Autonomy is not about replacing people.
It is about amplifying their decision-making capacity at scale.
Theory explains potential. Use cases prove value.
In 2026, Agentic AI in CRM is no longer a conceptual innovation — it is actively transforming revenue operations across SaaS, fintech, healthcare technology, manufacturing, and enterprise services in the United States.
Below are real-world applications where Autonomous CRM systems are delivering measurable impact.
One of the most powerful use cases of AI agents for sales is intelligent lead qualification.
Traditional systems rely on:
Agentic systems evaluate:
Instead of assigning a score once, the system continuously recalculates opportunity value.
For example:
If a mid-market SaaS buyer suddenly engages with pricing pages, attends a webinar, and downloads a comparison guide, the AI agent automatically reprioritizes that lead, triggers immediate outreach, and adjusts messaging tone.
This level of AI-driven sales workflow automation ensures that sales teams focus only on high-probability deals.
Result:
Pipeline stagnation is a silent revenue killer in US enterprises.
With AI-powered CRM software, agentic systems monitor:
If a deal shows early risk indicators, the AI agent can:
Instead of waiting for end-of-quarter surprises, Autonomous CRM systems proactively stabilize pipeline health.
This transforms CRM from reactive reporting to predictive protection.
Another emerging application of Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 is autonomous coaching.
Using call transcripts, sentiment analysis, and objection patterns, AI agents can:
For new SDRs, this reduces ramp-up time.
For experienced reps, it sharpens performance.
Rather than relying solely on manual call reviews, AI agents for sales provide real-time feedback loops — improving both individual and team performance.
This is especially impactful in high-growth SaaS companies where scaling sales teams quickly often creates consistency challenges.
Forecasting remains one of the most stressful responsibilities for US sales leaders.
Traditional forecasting depends on:
Agentic systems use:
With AI-driven sales workflow automation, forecasts update dynamically as new signals emerge.
If multiple late-stage deals show reduced engagement, the system adjusts revenue projections automatically and alerts leadership.
This creates:
For finance and RevOps teams, this alone justifies investment in advanced AI-powered CRM software.
Modern B2B buyers interact across channels:
Manually coordinating these touchpoints is inefficient and inconsistent.
Agentic systems coordinate engagement sequences autonomously.
Example:
If a prospect ignores email but engages on LinkedIn, the AI agent shifts outreach focus.
If webinar attendance increases interest, follow-ups accelerate automatically.
If engagement drops, the cadence adjusts.
This orchestration layer is a defining characteristic of next-generation Autonomous CRM systems.
Agentic CRM systems do not stop at acquisition.
They analyze:
If usage exceeds contract limits or adoption patterns increase, the system flags upsell opportunities automatically.
This is particularly powerful in subscription-based SaaS and fintech environments, where expansion revenue drives valuation.
Across all these use cases, one pattern emerges:
Traditional CRM documents activity.
AI-powered CRM analyzes activity.
But Agentic AI in CRM acts on activity autonomously.
These systems reduce decision latency, eliminate repetitive oversight, and continuously optimize revenue execution.
In 2026, the question for US companies is no longer whether AI belongs in CRM.
The real question is how quickly they can deploy intelligent, self-operating systems without falling behind competitors.
To fully understand the power of Agentic AI in CRM, it is essential to look beyond features and examine the architecture.
In 2026, Autonomous CRM systems are not powered by a single algorithm. They are built on layered AI infrastructure combining language models, decision engines, orchestration frameworks, and real-time data systems.
Below is a breakdown of the core technological components that enable true autonomy.
At the heart of modern AI-powered CRM software are advanced Large Language Models.
These models enable:
When integrated properly, LLMs allow AI agents to:
However, LLMs alone do not create autonomy. They provide reasoning capability — not structured decision-making.
One of the biggest risks in enterprise AI systems is hallucination or context drift.
To address this, advanced Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 implement Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
RAG enables AI agents to:
Before generating outputs or decisions, the system grounds itself in real-time, verified company data.
This significantly improves reliability in revenue-critical environments.
True AI agents for sales operate within coordinated systems.
Rather than a single AI model handling everything, modern architectures deploy multiple specialized agents, such as:
These agents communicate through orchestration layers that define:
This orchestration layer is what transforms automation into AI-driven sales workflow automation.
Instead of isolated tasks, workflows become goal-oriented and adaptive.
Traditional CRM systems rely on structured relational databases.
Agentic systems introduce vector databases, which enable:
For example:
If a prospect in the healthcare sector raises a pricing objection similar to a previously won deal, the AI agent can retrieve the successful negotiation pattern and recommend a comparable strategy.
This persistent contextual memory is foundational to Autonomous CRM systems.
Modern revenue systems operate in real time.
To enable continuous evaluation, agentic architectures integrate:
When a prospect opens an email, attends a webinar, or interacts with product demos, signals are processed immediately.
This allows AI agents to adjust outreach strategies dynamically — a key differentiator in competitive US markets.
The final layer of maturity in Agentic AI in CRM is adaptive learning.
Systems analyze:
Based on outcomes, AI models refine scoring mechanisms, communication styles, and prioritization rules.
Over time, the CRM becomes increasingly aligned with the organization’s unique sales DNA.
This is why companies serious about building an agentic AI powered CRM often require specialized engineering support, including:
Enterprise-level autonomy requires architectural precision — not just API integrations.
For US companies, especially in regulated industries, technical design must also address:
Well-designed AI-powered CRM software includes transparency layers that log AI-generated actions, ensuring accountability.
Autonomous CRM systems are not “smart plugins.”
They are structured AI ecosystems layered over CRM infrastructure.
Traditional CRM = Database.
AI-powered CRM = Analytics + Insights.
Agentic CRM = Reasoning + Execution + Continuous Optimization.
Understanding this technological foundation helps decision-makers evaluate vendors realistically — separating surface-level automation from true autonomous capability.
As US companies accelerate adoption of Agentic AI in CRM, one concern consistently surfaces at the executive level:
Can autonomous systems be trusted with revenue-critical data and decisions?
This is not a minor question. Sales CRMs contain:
Deploying Autonomous CRM systems without robust governance frameworks can introduce operational and legal risk. In 2026, responsible AI deployment is no longer optional — it is a board-level priority.
In the United States, AI-driven CRM implementations must account for:
Advanced AI-powered CRM software must provide:
When designed properly, AI-driven sales workflow automation can actually strengthen compliance by:
Autonomy, when governed correctly, improves transparency.
One of the biggest risks in deploying AI agents for sales is opaque decision-making.
For example:
If an AI system deprioritizes certain leads or reallocates pipeline focus, leadership must understand why.
Enterprise-grade Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 implement:
This ensures that autonomy does not mean lack of oversight.
In practice, well-designed Autonomous CRM systems operate under defined boundaries:
AI can recommend and execute actions within strategic guardrails — but high-risk decisions still require human validation.
This balance between automation and governance defines mature adoption.
AI models trained on historical sales data may unintentionally reinforce bias patterns.
Examples include:
Responsible deployment of Agentic AI in CRM requires:
US enterprises increasingly require AI systems to align with internal ethical AI frameworks before full deployment.
Ethical selling is not just reputational — it is regulatory and strategic.
Given the centrality of CRM to revenue operations, security architecture must include:
Organizations exploring building an agentic AI powered CRM often collaborate with experienced:
Security cannot be an afterthought layered onto AI. It must be embedded in the architecture from day one.
Despite rapid advances in AI-powered CRM software, mature organizations maintain human-in-the-loop systems for:
Agentic systems excel at pattern recognition and execution.
Humans remain essential for judgment, relationship nuance, and ethical oversight.
The most successful US companies treat AI agents as collaborators — not replacements.
The question is no longer whether Autonomous CRM systems are secure.
The real question is whether they are designed responsibly.
When implemented with:
Agentic AI in CRM becomes not only efficient — but trustworthy.
And in US enterprise environments, trust is the true competitive advantage.
To understand the real shift happening in 2026, it’s important to separate incremental automation from true autonomy.
Many US organizations believe they are “AI-enabled” because they use workflow triggers, predictive scoring, or automated email sequences. While these features improve efficiency, they do not represent Agentic AI in CRM.
The difference is structural.
Traditional automation executes predefined rules.
Agentic systems pursue revenue goals using contextual reasoning and adaptive decision-making.
Below is a clear breakdown of how Autonomous CRM systems differ from traditional CRM automation.
|
Dimension |
Traditional CRM Automation |
AI-Powered CRM Software |
Agentic AI in CRM |
|
Primary Function |
Execute predefined rules |
Provide predictive insights |
Make contextual decisions aligned with revenue goals |
|
Workflow Logic |
If/Then triggers |
Predictive scoring + automation |
Goal-driven multi-step orchestration |
|
Human Dependency |
High |
Moderate |
Strategic oversight only |
|
Lead Scoring |
Static or rule-based |
Predictive models |
Continuously adaptive with behavioral recalibration |
|
Deal Management |
Manual updates |
Assisted recommendations |
Autonomous risk detection and intervention |
|
Outreach |
Prebuilt sequences |
Personalized suggestions |
Context-aware, self-adjusting communication |
|
Forecasting |
Rep-submitted estimates |
Predictive analytics dashboards |
Dynamic, continuously updated autonomous projections |
|
Learning Mechanism |
None |
Periodic retraining |
Continuous feedback loop and self-optimization |
|
Execution Scope |
Task-level |
Task + insight level |
End-to-end AI-driven sales workflow automation |
Traditional CRM automation for sales teams focuses on task efficiency — reducing clicks and manual entries.
Agentic AI in CRM focuses on outcome optimization — increasing win rates, accelerating deal velocity, and reducing pipeline risk.
The system does not simply complete tasks. It evaluates whether those tasks move the deal forward.
Traditional automation depends on rigid logic trees.
Example:
“If no reply in 3 days → send follow-up email.”
In contrast, AI agents for sales evaluate:
Then determine whether to follow up, change messaging tone, escalate, or pause outreach.
This flexibility defines modern Intelligent CRM platforms 2026.
Standard CRM dashboards show what happened.
Autonomous systems act before problems escalate.
For example:
If multiple late-stage deals show declining engagement, an agentic system can:
This is the shift from visibility to proactive execution — a hallmark of advanced AI-powered CRM software.
Traditional automation improves efficiency by reducing repetitive effort.
Agentic autonomy creates leverage by allowing a smaller sales team to operate with:
In high-growth US tech environments, this difference directly impacts revenue scalability.
Many organizations mistakenly assume that upgrading automation equals modernization.
However, as competition intensifies and buyers become more sophisticated, incremental improvements are no longer sufficient.
Companies adopting true Autonomous CRM systems gain:
The shift from rule-based automation to agentic autonomy is not cosmetic.
It represents a structural redesign of how revenue operations function.
In 2026, the companies that understand this distinction will build systems that act.
Those that do not will continue managing dashboards instead of driving outcomes.
For US sales leaders, innovation without measurable return is noise.
The rapid adoption of Agentic AI in CRM is not happening because it is futuristic — it is happening because it produces quantifiable financial outcomes.
In 2026, companies implementing Autonomous CRM systems are reporting gains across efficiency, revenue velocity, forecasting accuracy, and operating margin.
Below is how ROI is materializing in real business terms.
In traditional environments, sales representatives spend 25–40% of their time on:
By implementing AI-powered CRM software with agentic capabilities, companies are reducing manual CRM management time by 30–50%.
The result:
For mid-market SaaS companies, this alone can represent millions in incremental annual revenue without increasing hiring.
Speed remains one of the strongest predictors of conversion.
With AI-driven sales workflow automation, organizations are achieving:
Instead of waiting hours or days for manual action, AI agents initiate engagement within minutes when buying signals spike.
Companies using advanced AI sales automation tools are reporting:
The impact compounds across the funnel.
Agentic systems continuously analyze:
By proactively intervening, AI agents for sales help prevent stalled opportunities.
Organizations deploying Autonomous CRM systems have observed:
Even a 5–10% improvement in close rate can dramatically alter annual revenue performance in enterprise environments.
Forecasting accuracy directly affects:
Traditional forecasting often relies on rep-submitted confidence levels — a method prone to bias.
By leveraging behavioral data, historical trends, and dynamic probability modeling, Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 provide continuously updated revenue projections.
US companies adopting Agentic AI in CRM report:
For publicly accountable organizations, this level of predictability has significant strategic value.
Sales headcount expansion is expensive.
By integrating advanced CRM automation for sales teams, companies can:
Instead of hiring additional personnel to manage complexity, organizations leverage agentic systems to amplify existing teams.
This shift from labor-based scaling to leverage-based scaling is one of the defining ROI factors of 2026.
Perhaps the most underestimated ROI driver is learning accumulation.
Because AI-powered CRM software continuously refines models based on win/loss data and engagement outcomes, performance improves over time.
Each quarter, the system becomes more aligned with:
This compounding intelligence effect transforms CRM from a static tool into a strategic asset.
Traditional CRM systems store data.
Autonomous systems generate leverage.
Companies implementing AI-driven sales workflow automation are not just improving efficiency — they are reshaping revenue economics.
The ROI of Agentic AI in CRM in 2026 can be summarized across four dimensions:
In competitive US markets, those four factors determine long-term growth sustainability.
The question is no longer whether AI belongs inside CRM.
The question is how quickly organizations can operationalize autonomy before competitors widen the performance gap.
Understanding the value of Agentic AI in CRM is one thing. Implementing it responsibly and effectively is another.
For US organizations, especially mid-market and enterprise companies, transitioning toward Autonomous CRM systems requires structured planning, technical clarity, and cross-functional alignment.
Below is a strategic roadmap for leaders serious about building long-term AI capability rather than layering superficial automation.
Not every organization requires full workflow autonomy on day one.
There are typically three maturity levels:
Level 1 – Assistive Intelligence
AI supports reps with recommendations, lead scoring, and drafting assistance.
Level 2 – Task-Level Autonomy
AI agents independently execute specific workflows such as follow-ups, prioritization, and deal risk alerts.
Level 3 – Workflow-Level Autonomy
Coordinated multi-agent systems manage pipeline prioritization, forecasting updates, outreach sequencing, and risk intervention dynamically.
Before investing, leadership should define:
This prevents over-engineering while ensuring ROI alignment.
Not all CRM systems are architecturally ready for agentic layering.
A proper audit should evaluate:
Since AI-driven sales workflow automation depends heavily on data quality, incomplete or inconsistent CRM records can undermine autonomy.
Organizations exploring broader AI Agent Adoption in tech companies strategies often begin with this data foundation review.
Autonomy is only as strong as the data it reasons with.
Companies typically choose one of three paths:
Fast implementation but limited customization.
Integrating agentic capabilities through custom APIs and AI orchestration.
Designing architecture aligned with unique sales workflows.
Organizations with complex pipelines or regulated environments often lean toward custom solutions through:
This approach allows deeper integration, stronger security alignment, and long-term scalability.
Instead of organization-wide deployment, begin with:
Track measurable KPIs:
Pilots allow calibration before scaling autonomy across the organization.
This measured rollout reduces operational risk while validating ROI.
Even the most advanced Autonomous CRM systems require governance.
Implementation plans must define:
Human-in-the-loop design remains essential, particularly in enterprise and regulated industries.
Autonomy should increase control, not reduce accountability.
Organizations serious about building an agentic AI powered CRM treat it as a living system.
This includes:
The competitive advantage compounds when AI agents learn from real revenue outcomes over time.
Implementing Agentic AI in CRM is not a technology project. It is a revenue architecture transformation.
Sales leaders must shift from asking:
“How can we automate more tasks?”
to asking:
“How can we redesign our revenue engine around autonomous execution?”
Companies that approach this strategically — rather than reactively — are building scalable systems capable of adapting to market volatility, buyer complexity, and growth pressure.
In 2026, autonomy is not a luxury feature.
It is a structural advantage.
If 2026 marks the mainstream adoption of Agentic AI in CRM, the years beyond will define its full strategic impact.
What we are witnessing today is only the first phase of autonomy — task execution and workflow orchestration. The next evolution of Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 will extend far beyond internal sales support.
The CRM is no longer becoming smarter.
It is becoming self-optimizing infrastructure.
Below are the major shifts already emerging.
Future Autonomous CRM systems will not just execute workflows — they will continuously redesign them.
Instead of relying on static playbooks, agentic systems will:
The CRM will evolve from a reactive tool into a system that actively experiments and improves revenue strategy without waiting for quarterly reviews.
This creates a compounding intelligence loop that strengthens performance over time.
Today, AI assists outbound campaigns.
Beyond 2026, it will independently orchestrate them.
Advanced AI agents for sales will:
This will move AI-driven sales workflow automation from supportive engagement to proactive revenue generation.
In competitive US markets, the ability to detect and act on opportunity before competitors do will redefine sales advantage.
As businesses increasingly adopt AI systems, future CRM environments may involve AI agents interacting with AI-enabled buyer systems.
Potential developments include:
While human oversight will remain essential for strategic decisions, routine negotiations may become partially autonomous.
This represents a significant expansion of what AI-powered CRM software can influence.
The next generation of Autonomous CRM systems will integrate more tightly with:
Rather than operating as a standalone revenue database, CRM will become part of a unified enterprise intelligence layer.
This convergence will allow AI systems to:
In this environment, CRM autonomy becomes organizational autonomy.
Future Agentic AI in CRM systems may simulate strategic outcomes before decisions are implemented.
For example:
Using historical data, market indicators, and behavioral analytics, CRM platforms may offer scenario modeling as a built-in capability.
This shifts CRM from an operational tool to a strategic advisory engine.
As autonomy deepens, governance frameworks will mature alongside it.
Expect future Intelligent CRM platforms 2026 and beyond to include:
Trust will become a competitive differentiator.
Companies that implement responsible Agentic AI in CRM architectures will be better positioned to scale in regulated industries and enterprise markets.
Beyond 2026, CRM will no longer be defined by data entry, dashboards, or reporting modules.
It will function as:
Organizations that begin building autonomy today are not just improving efficiency — they are laying the foundation for adaptive, intelligent revenue ecosystems.
The companies that hesitate may find themselves competing against systems that operate faster, learn continuously, and execute without friction.
The future of CRM is not incremental automation.
It is coordinated intelligence at scale.
For years, CRM systems have been positioned as productivity tools. They helped sales teams track interactions, store contacts, and generate reports. But in practice, they also created operational drag — requiring constant updates, manual oversight, and repetitive administrative effort.
In 2026, that model is becoming obsolete.
The emergence of Agentic AI in CRM marks a structural shift in how revenue organizations operate. The CRM is no longer just a system of record. It is becoming a system of execution — capable of reasoning, acting, and continuously optimizing outcomes.
Traditional CRM automation for sales teams improved efficiency.
AI-powered CRM software improved insights.
But Autonomous CRM systems are redefining responsibility.
They qualify leads dynamically.
They detect pipeline risk early.
They orchestrate outreach across channels.
They update forecasts in real time.
They learn from win/loss outcomes and refine strategy continuously.
This evolution represents a move from data entry to decision delegation.
For US sales leaders facing rising acquisition costs, tighter margins, and increased accountability, autonomy is not about replacing human talent. It is about amplifying it.
Sales professionals remain responsible for relationships, negotiation, and strategic thinking.
AI agents handle repetition, pattern detection, and execution at scale.
Organizations that embrace AI-driven sales workflow automation are gaining leverage — reclaiming time, increasing close rates, and building predictable revenue systems. Those that delay risk operating at human speed in a market that increasingly moves at machine speed.
The question is no longer whether AI belongs inside CRM.
The question is whether your CRM is ready to act — not just record.
In the years ahead, competitive advantage will not come from having more data.
It will come from having systems capable of making better decisions with it.
That is the promise — and the power — of Agentic AI in CRM.
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation
Open roles, referrals, campus hiring