Sales Team
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation

What if the future of trust, security, and global digital transactions was built on a technology that never sleeps, can’t be altered, and works without any central authority?
That’s the transformative power of blockchain technology, a system that is reshaping industries, empowering businesses, and redefining how data, assets, and value move across digital ecosystems.
Once known only for powering Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved far beyond cryptocurrencies. Today, it stands as a foundational digital infrastructure used by governments, enterprises, financial institutions, and global innovators. From secure financial transactions to transparent supply chains, blockchain’s real potential lies in its ability to deliver trust, transparency, and efficiency at scale.
Blockchain technology is a highly secure, transparent, and decentralized digital ledger system. Instead of storing information on a single central server, it distributes identical copies of data across thousands of computers around the world. Because every computer, or node, holds the same record, the information becomes extremely difficult to alter or manipulate. This decentralized structure increases trust, enhances security, and ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and tamper-proof.
To understand the blockchain definition more clearly, think of it as a digital ledger that operates across multiple nodes and records information in a way that prevents tampering, deletion, or unauthorized modification. Each record, or block, is securely connected to the next using strong cryptographic techniques, forming an unbreakable chain of data. This is why blockchain is considered one of the most reliable technologies for secure transactions, transparent data sharing, and long-term information integrity.
Blockchain technology works on a strong foundation of features that make it more secure, transparent, and trustworthy than traditional databases. These core elements ensure that data stored on a blockchain is protected from tampering, easily verifiable, and accessible without depending on a single central authority. Understanding these key elements helps explain why industries worldwide—from finance and healthcare to logistics and government—are rapidly adopting blockchain as a reliable digital infrastructure.
Now, let’s explore the major components that make blockchain so powerful:
Traditionally, databases store all information in a single centralized location, such as a bank server, corporate system, or government registry. This centralization increases risks like data loss, unauthorized manipulation, hacking, and system-wide failures.
Blockchain overcomes these challenges through decentralization, meaning data is distributed across hundreds or even thousands of nodes instead of relying on one authority. Each node holds a copy of the ledger, making the system more secure and resilient.
Key benefits of decentralization include:
This concept gained widespread recognition with the Bitcoin chain, which demonstrated how digital value could be exchanged securely without banks or intermediaries.
One of the most powerful advantages of blockchain is its built-in transparency. Every transaction added to the blockchain is visible to all authorized participants, creating an environment of trust and openness.
Transparency ensures:
Public blockchains (like Bitcoin or Ethereum) provide complete openness, while private blockchains offer controlled visibility. This makes blockchain suitable for industries such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare where accountability and traceability are essential.
Immutability means that once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be changed, reversed, or deleted. This property is one of the main reasons blockchain is considered highly trustworthy.
Immutability is achieved using:
If someone tries to modify even a tiny piece of information, the system immediately detects inconsistencies because the altered data will no longer match the cryptographic pattern stored across other nodes. This makes blockchain extremely reliable for storing sensitive, high-value, or legally significant information such as financial records, identity data, supply chain details, and medical histories.
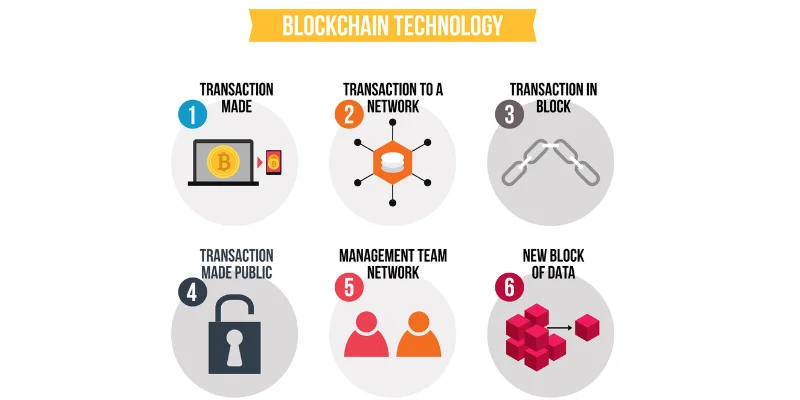
Blockchain appears complicated at first, but it functions through a logical, sequential, and highly secure process. Understanding each step helps reveal why blockchain is so trusted for data security, transparency, and decentralization. Let’s explore each stage in detail.
The first step in blockchain begins with a transaction, which represents any activity a participant wants to record on the blockchain. Transactions can take many forms, such as:
Each transaction includes crucial information such as the sender, receiver, amount, timestamp, and other metadata. Until this transaction is verified by the network, it exists only as a pending record, not yet officially part of the blockchain.
Once the transaction is created, it is broadcast to the blockchain network, which is composed of many computers called nodes. Each node receives a copy of the transaction and prepares to validate it.
Broadcasting ensures:
This step is crucial because blockchain does not rely on a central server; it depends on the collective verification by all nodes to maintain trust and integrity.
After broadcast, nodes validate the transaction using a consensus mechanism. Consensus ensures that only legitimate, accurate transactions are added to the blockchain, preventing fraud, double-spending, or tampering.
Common consensus mechanisms include:
1. Proof of Work (PoW)
2. Proof of Stake (PoS)
3. Proof of Authority (PoA)
4. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
By validating transactions collectively, the blockchain network ensures accuracy, integrity, and trustworthiness of all data recorded.
Once transactions are validated, they are grouped together into a block. Each block contains:
The inclusion of the previous block’s hash ensures that each block is cryptographically linked, making it nearly impossible to alter data without breaking the entire chain.
After the block is created, it is added to the existing blockchain, forming a chain of blocks. Each block’s hash references the hash of the previous block, creating an immutable and chronological record of all transactions.
This linking ensures:
This is why it is called a “blockchain”—a series of connected blocks forming a secure digital ledger.
Finally, the updated blockchain is synchronized across all nodes in the network. Every participant receives the latest version of the ledger, ensuring that:
This step completes the transaction cycle, guaranteeing security, trust, and reliability without the need for a central authority or intermediary.
Blockchain is a versatile technology, and its implementation varies depending on business needs, security requirements, and governance policies. Different industries require varying levels of openness, privacy, and control, which has led to four main types of blockchain: public, private, consortium, and hybrid. Each type has distinct characteristics, advantages, and ideal use cases.
Public blockchains are fully decentralized networks open to anyone. In these blockchains, anyone can read, write, or validate transactions without needing permission. This openness ensures transparency, decentralization, and security through a distributed consensus mechanism.
Examples:
Public blockchains are fully decentralized networks open to anyone. In these blockchains, anyone can read, write, or validate transactions without needing permission. This openness ensures transparency, decentralization, and security through a distributed consensus mechanism.
Examples:
Common Uses:
Advantages of Public Blockchains:
Limitations:
Public blockchains are ideal for systems where openness, trust, and decentralization are critical, such as cryptocurrencies, digital assets, and community-driven platforms.
Private blockchains are restricted networks, where only authorized participants can read, write, or validate transactions. These blockchains are typically controlled by a single organization and are designed to maintain confidentiality, efficiency, and control over sensitive data.
Used By:
Benefits of Private Blockchains:
Private blockchains are particularly suitable for organizations that need blockchain security and immutability without exposing sensitive business data to the public.
Consortium blockchains are semi-decentralized networks controlled by a group of organizations, rather than a single entity. This type is common in industries where collaboration between multiple stakeholders is essential.
Best For:
Advantages:
Consortium blockchains are ideal for industries requiring cooperation and transparency among trusted parties, such as global trade networks, financial institutions, and logistics companies.
Hybrid blockchains combine features of public and private blockchains, offering both transparency and controlled access. Organizations can keep sensitive data private while still leveraging the benefits of a public blockchain for transparency and traceability.
Uses:
Advantages of Hybrid Blockchains:
Hybrid blockchains provide organizations with customizable solutions, making them ideal for large-scale enterprises, supply chains, and governmental networks that require both openness and confidentiality.

Cryptocurrency and blockchain are closely connected, but not identical. Blockchain serves as the technology, while cryptocurrency is one of its applications.
The Bitcoin chain was the first real-world demonstration of blockchain’s power. Today, thousands of cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain for trust, transparency, and decentralization.
Blockchain is considered a revolutionary technology because it provides benefits that traditional systems cannot match. Its unique combination of decentralization, transparency, security, and automation makes it a vital tool for businesses, governments, and industries worldwide. Let’s explore the key benefits in detail:
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its high level of security. Every transaction on a blockchain is encrypted using advanced cryptography, which makes it extremely difficult for hackers to alter or tamper with the data.
In addition:
Real-World Example: Banks and financial institutions use blockchain to secure digital payments and transactions, drastically reducing the risk of fraud and cyber-attacks. Similarly, healthcare organizations leverage blockchain to secure sensitive patient records, ensuring privacy and compliance. Blockchain provides full visibility of transactions, creating trust among all participants in a network. Each transaction is recorded on a public ledger (or a controlled private ledger) and can be traced in real-time. Benefits of this transparency include: Real-World Example: Supply chain companies use blockchain to make production and shipment data visible to all stakeholders, allowing customers to verify the origin of products, such as organic food or luxury goods. Blockchain can significantly reduce operational costs by eliminating intermediaries, manual reconciliation, and redundant paperwork. Traditional systems often involve banks, auditors, and administrative staff, all of which add to the cost of transactions. Blockchain reduces costs related to: Real-World Example: Cross-border payments using traditional banking can take days and incur high fees. Blockchain enables near-instant settlements with lower transaction costs, as demonstrated by companies like Ripple in the financial sector. Traditional banking systems, especially for international transactions, often require days for processing due to intermediaries and cross-border delays. Blockchain accelerates transaction processing, making it almost instantaneous in many cases. Real-World Example: Companies transferring funds between global subsidiaries can use blockchain to settle payments within minutes, rather than waiting several business days. Once information is added to a blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This immutability ensures: This is achieved through: Real-World Example: Land registries in countries like Sweden and India are exploring blockchain to create tamper-proof property records, eliminating fraud and disputes over ownership. Blockchain provides end-to-end traceability, which is especially valuable in supply chains, pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and any industry where verifying provenance is critical. Blockchain can track: Real-World Example: Pharmaceutical companies use blockchain to trace medicines from manufacturer to distributor to pharmacy, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeit drugs. Similarly, luxury brands track products to prove authenticity and prevent fraud. Blockchain technology is no longer confined to cryptocurrency. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature makes blockchain development solutions highly applicable across multiple sectors. From finance to healthcare, supply chains, and government services, blockchain is transforming traditional processes into efficient, tamper-proof digital systems. Here’s a detailed look at the most impactful applications of blockchain across industries: The financial sector was among the first to adopt blockchain due to its need for secure, fast, and transparent transactions. Key Applications: Real-World Examples: Benefit: Faster, more secure, and cost-efficient financial operations. Blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain operations by providing full visibility and traceability of goods. Benefits: Real-World Examples: Benefit: Increased trust, efficiency, and safety across global supply chains. Blockchain ensures the security, privacy, and integrity of medical data, which is critical in healthcare. Use Cases: Benefit: Protects patient privacy, reduces fraud, and streamlines healthcare operations. Blockchain simplifies complex real estate transactions and reduces paperwork and disputes. Applications: Benefit: Faster, more secure, and transparent real estate transactions. Governments are exploring blockchain for secure, transparent, and efficient public services. Examples of Use: Benefit: Improves trust, reduces corruption, and increases public accountability. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are digital assets whose ownership and authenticity are verified using blockchain. Benefits: Use Cases: Digital art, music, gaming items, virtual real estate, and collectibles. Benefit: Creates a secure and verifiable digital ownership ecosystem. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain. They execute automatically when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Applications: Benefit: Reduces manual intervention, prevents disputes, and improves operational speed. Different blockchain platforms serve different business needs, depending on transaction speed, scalability, and functionality. Popular Platforms: Benefit: Organizations can choose platforms tailored to their specific performance and business requirements. As blockchain adoption grows, businesses need professional blockchain development services to implement secure and scalable solutions. Services Provided by Blockchain Development Companies: Specialized Blockchain Development Solutions are offered for sectors like finance, healthcare, supply chains, and government systems. These solutions help organizations transition from traditional centralized systems to decentralized, secure, and efficient digital processes. Benefit: Ensures businesses can leverage blockchain for enhanced efficiency, security, and transparency. Blockchain is increasingly becoming the digital backbone of global systems. Its influence will continue to grow across industries and everyday digital interactions. Future Trends: Impact: Blockchain will redefine digital trust, streamline processes, and create a more secure, transparent, and decentralized digital economy. Blockchain is more than a technological trend, it is a revolutionary shift in how data, value, and digital identities are secured and shared. Whether in finance, healthcare, government, real estate, or supply chains, blockchain delivers unmatched transparency, immutability, and security that traditional systems cannot offer. As organizations adopt decentralized technology, choosing the right blockchain development companies and implementing effective blockchain development solutions becomes essential for long-term success. For businesses seeking reliable, scalable, and innovative blockchain systems, SISGAIN stands as a trusted partner committed to delivering cutting-edge digital solutions and future-ready transformation.2. Complete Transparency
3. Reduced Costs
4. Faster Transactions
5. Immutability
6. Traceability
Top Use Cases of Blockchain Across Industries

1. Blockchain in Finance
2. Supply Chain Management
3. Healthcare
4. Real Estate and Property Management
5. Government and Public Sector
6. NFTs and Digital Assets
7. Smart Contracts for Business Automation
8. Leading Blockchain Platforms
9. Blockchain Development: Why Businesses Need It
10. The Future of Blockchain Technology
Conclusion
Project quotes, partnerships, implementation
Open roles, referrals, campus hiring